Everything You Need to Know About Temporary Powerhouse Visas
- Business Immigration
- News
by Natalie McQuilkin
Since the creation of temporary work visas, many industries and businesses have relied on foreign workers to fill seasonal or temporary jobs. Temporary work visas provide a two-fold benefit: they provide secure, good-paying work for foreign nationals, and they help improve the U.S. economy by filling short-term positions that might not otherwise be filled.
In this blog post, we’ll touch on three of the most common temporary work visas:
- the H-2A visa, which is geared for seasonal agricultural workers,
- the H-2B visa, which is designed for seasonal non-agricultural workers, and
- the H-1B visa, which accommodates workers in specialty occupations.
We’ve touched on these visas in our blog posts on the hospitality industry and the restaurant industry, but this time, we’ll dive into the details of each visa so you can learn which of these visas is the best fit for your company.
The H-2A Visa
The H-2A visa is specifically targeted to fill temporary agricultural roles. This could be applied to when an apartment complex needs to be built, or when a specific crop needs to be harvested. According to U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), the most common jobs for the H-2A visa fall under farming, fishing, and forestry, as well as construction and extraction.[1] These jobs can range from working on farms, operating agricultural equipment, or truck driving.[2]
The table below, which was pulled from the USCIS H-2A Employer Data Hub, showcases the top companies that petitioned the most H-2A visas as of June 2023.
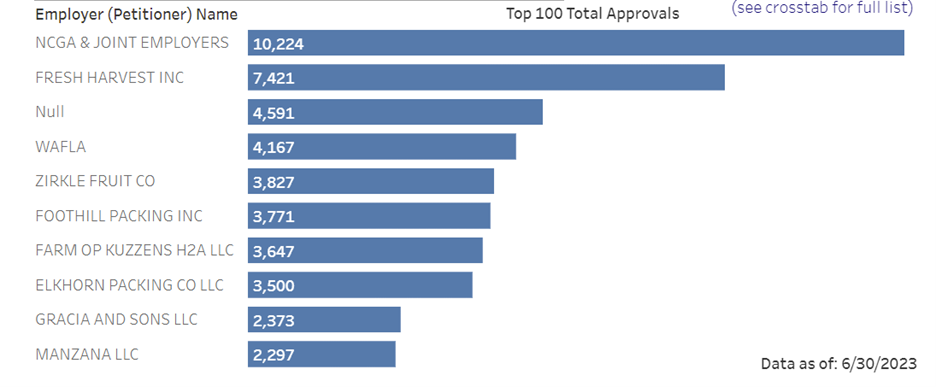
This table provides insight into what types of companies rely on H-2A petitions to fill thousands of temporary jobs.
The Petition Process
This visa, along with the others that will be covered in this post, requires the employer to follow a specific petition process. One of the main reasons for this process hinges on the need to ensure there are no U.S. workers “able, willing, qualified, and available” for the job and that U.S. workers’ wages and working conditions will not be “adversely affected” if foreign nationals are hired to work in similar roles.[3]
To begin petitioning a foreign national for the H-2A visa, the employer must first obtain a prevailing wage determination, which establishes the minimum wage that the employer can pay the foreign worker. This is to ensure that U.S. employees working in similar positions will continue to be paid adequately. After this, the employer can file a job order with the State Workforce Agency. While filling out the job order, it’s imperative that the employer provides accurate information regarding the foreign national’s name, the projected salary, and the job requirements. Then, the H-2A application for the temporary employment certification can be filed.
As an attempt to hire U.S. workers for a temporary agricultural job, the employer must prove he or she has attempted and failed to recruit U.S. candidates for the job in question. If there are no acceptable U.S. candidates, the employer can create and submit a recruitment report to demonstrate that there were no qualified U.S. workers willing to take the job. After this is submitted to the Chicago National Processing Center (NPC), Chicago NPC will provide a final determination notice, which grants approval or denial. If approved, the employer will then submit the Petition for a Nonimmigrant Worker (Form I-129) with the temporary labor certification and any additional documentation to USCIS. After Form I-129 is approved, H-2A workers living outside of the U.S. must then apply for the H-2A visa with the Department of State at a U.S. Embassy or a foreign consulate.
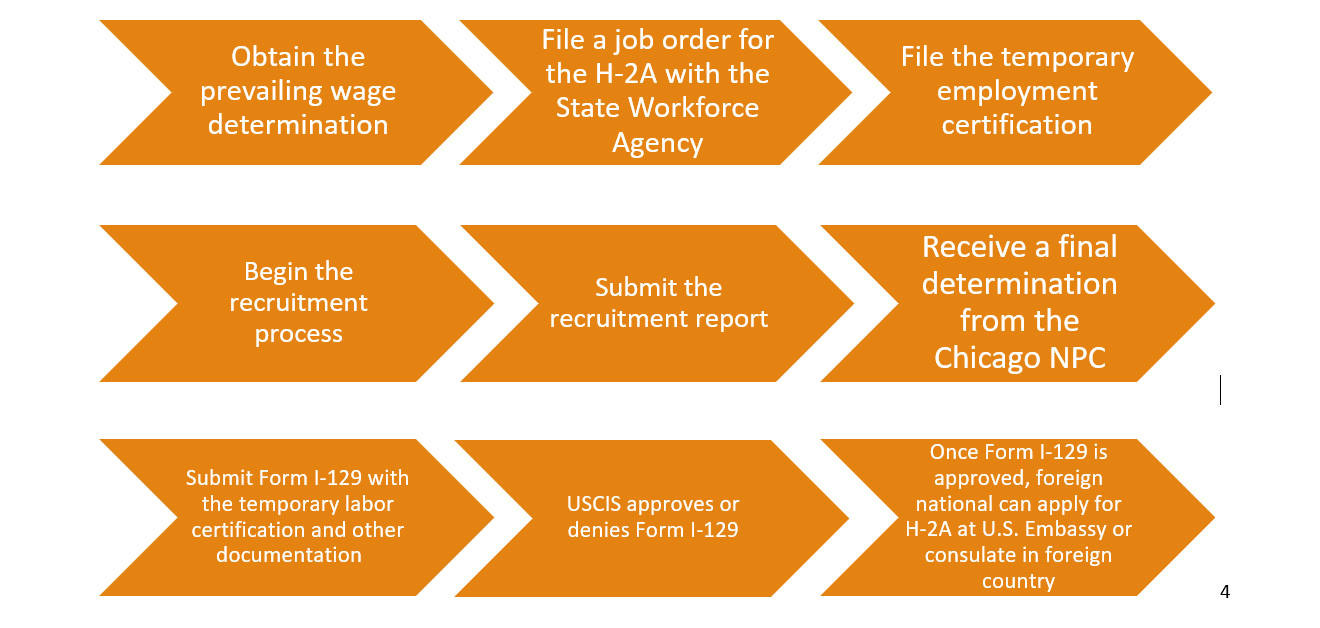
Although the initial steps of the H-2A visa are lengthy, having the petitions processed is quite fast due to the temporary nature of this visa. As of December 2023, the California Service Center is processing the Form I-129 in just 15 days .[5]
Once the petition is approved, the beneficiary can stay in the United States for the term listed on their labor certification. This period of stay can be extended in 1-year increments until the beneficiary has been in the U.S. for three years, according to USCIS. While the beneficiary is living and working in the U.S., his or her spouse and unmarried children younger than 21 can also join the foreign national.
Other Important Considerations for the H-2A
Along with following the multi-step petition and application process, employers must also abide by other guidelines set forth by USCIS:
- The employer must provide free housing for workers, and the housing must meet the Department of Labor’s housing condition requirements, which can be found here.[6]
- The employer must provide three free meals a day to employees or provide free and convenient cooking areas or kitchen facilities. You can learn more about these requirements by reviewing this Department of Labor fact sheet.[7]
The H-2B Visa
The H-2B visa is a temporary, nonagricultural visa that accommodates businesses interested in filling seasonal or short-term positions. Each fiscal year, 66,000 visas are made available, with 33,000 visas designed for the first half of the fiscal year, and the remaining 33,000 visas corresponding to the second half of the fiscal year. Because of this visa’s high demand, the cap is reached quickly each year. In fiscal year 2024, the 33,000 visa cap was reached on October 11, 2023—just 10 days after the fiscal year began.[8]
What Kind of Industries and Jobs Correlate with the H-2B Visa?
Because this visa does not require specialized skills or a degree, it’s great for recruiting workers to take on jobs that do not require much experience, such as dishwashing, housekeeping, serving, packing, and more. In June 2023, the top industries that petitioned for H-2B visas included administration, support, waste management, remediation services, and manufacturing.[9]
Below is a breakdown from the USCIS Employer Data Hub featuring the top companies that petitioned for H-2B visas in June 2023.
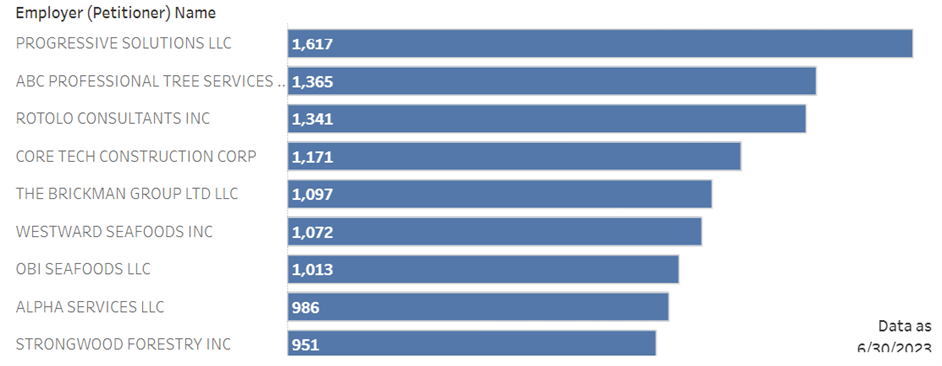
The Petition Process
As with the H-2A visa, the employer must fulfill many requirements to petition a foreign national. The petitioner must fall under one of these categories to petition a foreign national:
- The employer only needs to hire temporary workers for a one-time event of short duration. One example of this is hiring additional servers for a large celebration commemorating a company’s success.
- The employer needs to hire temporary workers for recurring seasons and peak seasons or events. This could include hiring lifeguards and ski instructors during the summer and winter seasons.
- The employer only needs to hire temporary workers intermittently, and permanent, full-time employees will not perform the same jobs as the temporary worker. An example of this is hiring foreign nationals to stock merchandise during busy periods while permanent employees fulfill other job duties.
The H-2B petitioning process is like the H-2A petitioning process. The employer must submit a temporary labor certification to the Department of Labor to provide evidence that the foreign worker and U.S. workers in the same position will be paid fairly. Once the certification is approved, the petitioner can file Form I-129 with USCIS. After this is approved, the beneficiary can apply for his or her visa or seek admission into the U.S.
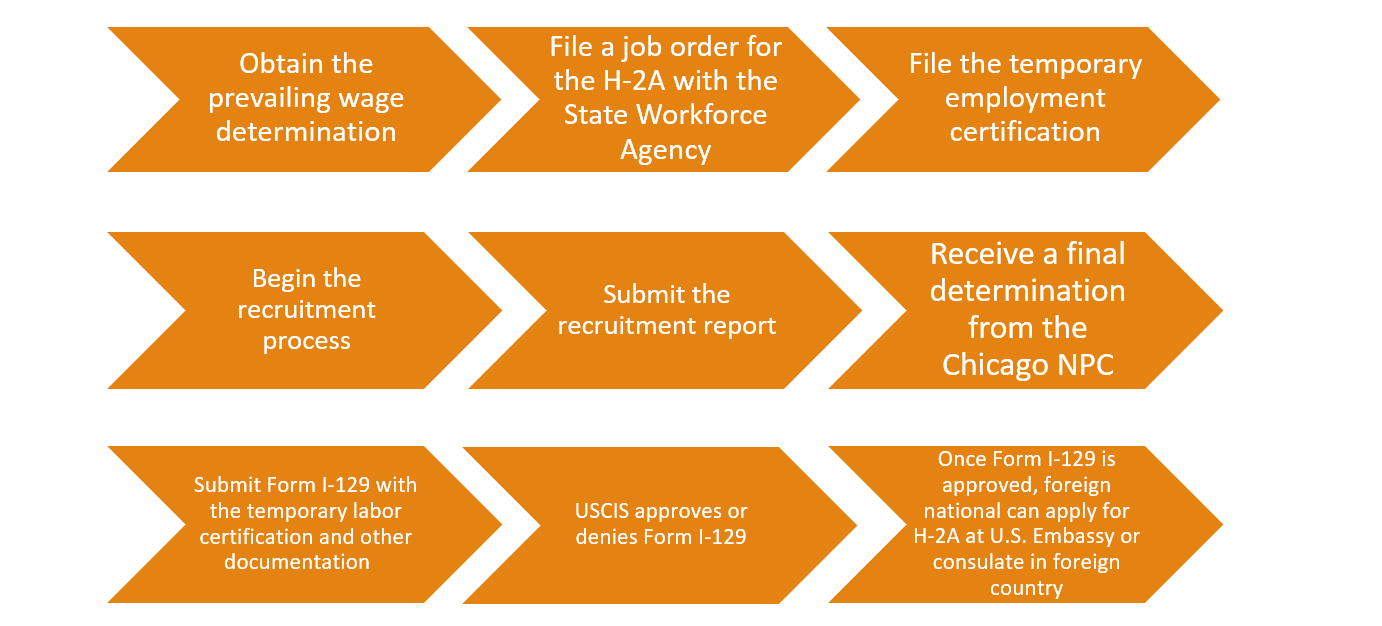
The period of stay for the temporary employee depends on the labor certification that their employer submits, but foreign nationals can stay for as long as three years on the H-2B visa. Like the H-2A visa, the beneficiary’s spouse and unmarried children younger than 21 can join them in the United States with H-4 visas.[10]
As of December 2023, the California Service Center is processing applications in just one week, and the Vermont Service Center is processing applications in five weeks.[11]
What is the H-1B Visa?
Created through the Immigration Act of 1990, the H-1B visa is designed to accommodate foreign nationals with specialty occupations.[12] According to USCIS, to be considered a “specialty occupation,” the job “requires theoretical and practical application of a body of highly specialized knowledge,” and it requires at least a U.S. bachelor’s degree or its equivalent. This can also include certifications or licensing.
As of July 2023, the most common industries that petitioned beneficiaries for an H-1B visa included professional, scientific, and technical services; retail trade; information; manufacturing; and finance and insurance.
Within these fields, several well-known companies top the charts of businesses petitioning for foreign nationals:
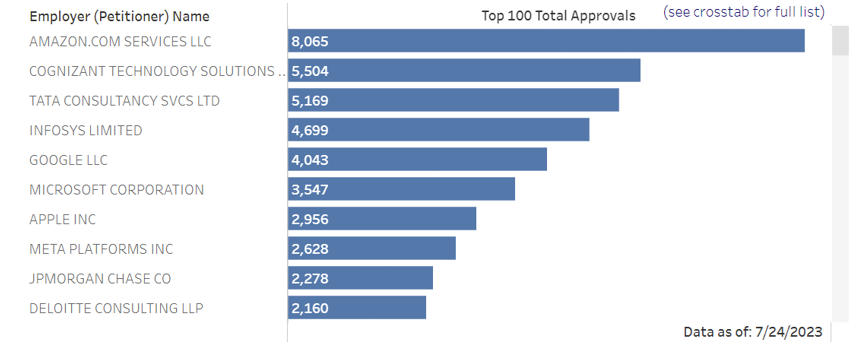
However, just because a certain industry doesn’t fall under the most common industries, that doesn’t mean it can’t be utilized for the H-1B visa. In past blog posts, we have discussed how the H-1B visa can be used in the restaurant industry and hospitality industry, too.
Benefits of the H-1B Visa
This popular visa has several benefits. One stand-out characteristic of this visa is that it is a dual-intent visa, meaning that the beneficiary can live and work in the U.S. temporarily, or he or she can apply for a green card while using the visa. This dual-intent quality is very appealing for both those who just want to gain work experience in the United States, or for those interested in creating a future for themselves in the United States permanently.
The H-1B visa also has a “portability” aspect, meaning that an H-1B worker can change jobs and be petitioned by a new employer while living in the United States, which eliminates the risk of the foreign national being “out of status,” according to the Department of Labor.[13]
Although the period of stay for the beneficiary is dependent on the labor condition application that the petitioner submits to the Department of Labor, foreign nationals typically stay for about three years. That period of stay can be extended to six years, if necessary. This provides stable employment for the beneficiary and ensures the business that a specific role will remain filled for a stretch of time.
Another great benefit of this visa is that the foreign national’s spouse and unmarried children younger than 21 can join them in the United States using H-4 visas. A final plus for this type of visa is that the application is processed more quickly than most. As of December 2023, it is taking about 1.5 to 6.5 months to process H-1B visas in at the California, Vermont, Nebraska and Texas service centers.[14]
The H-1B Visa Cap
At the start of each fiscal year, the U.S. government allots 65,000 H-1B visas for bachelor’s degree holders and 20,000 additional H-1B visas for those who have a master’s degree or higher. However, because of this visa’s popularity, the U.S. government quickly receives more than 85,000 applications. In fiscal year 2024, 780,884 applications were submitted for the H-1B visa, which was a 61 percent jump from the previous fiscal year.[15] Because this visa is highly sought after, a lottery system is used to randomly determine which applicants can be petitioned.
There are some instances where the cap doesn’t apply, such as when “an employer sponsoring you is an institution of higher education, a nonprofit organization connected to an institute of higher education, or a government research organization.” [16]
The Petitioning Process
If the employer is subject to the H-1B visa cap, it’s important to know that there is a specific timeline to follow for the H-1B visa petitioning process. The earliest that petitioners can register for the H-1B visa is February 21. At 12 p.m. eastern time on March 1, the registration period opens, and the registration period closes at 5 p.m. eastern time on March 20.
When registering for the H-1B visa, the employer must note that the beneficiary will start on October 1 or later. If the employer is selected from the lottery, the business must begin obtaining the prevailing wage and labor condition application. Then, the business can file the Form I-129 with USICS. Employers should know that only one foreign national can be named per petition.[17]
I’m Interested in Hiring Foreign Workers! What Are the Next Steps?
Petitioning a foreign national through one of these powerhouse visas is a great way to provide stability for your business during high-volume periods or busy seasons. Because the petition process can be a complicated one, it’s imperative that you have a trusted business immigration attorney by your side. If you’re interested in petitioning a foreign national for the H-2A, H-2B, or H-1B visa, schedule a consultation with Eagan Immigration’s business attorney, Hannah Whaley. Click this link to get started or call our office at (202) 709-6439.
[1] H-2A Employer Data Hub, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, Jun. 30, 2023, H-2A Employer Data Hub | USCIS, (last visited: Nov. 22, 2023).
[2] Hannah Whaley, The Powerhouse Visas for U.S. Businesses: H-1B, H-2A, and H-2B, Eagan Immigration, Nov. 30, 2023, The Powerhouse Visas for U.S. Businesses: H-1B, H-2A and H-2B – YouTube.
[3] H-2A Temporary Agricultural Workers, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, Nov. 8, 2023, H-2A Temporary Agricultural Workers | USCIS, (last visited: Dec. 4, 2023).
[4] Hannah Whaley, The Powerhouse Visas for U.S. Businesses: H-1B, H-2A, and H-2B, Eagan Immigration, Nov. 30, 2023, The Powerhouse Visas for U.S. Businesses: H-1B, H-2A and H-2B – YouTube.
[5] Processing Times, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, Processing Times (uscis.gov), (last visited Dec. 4, 2023).
[6] Fact Sheet #26G: H-2A Housing Standards for Rental and Public Accommodations, U.S. Department of Labor, Nov. 2022, Fact Sheet #26G: H-2A Housing Standards for Rental and Public Accommodations | U.S. Department of Labor (dol.gov).
[7] Fact Sheet #26D: Meal Obligations for H-2A Employers, U.S. Department of Labor, Nov. 2022, Fact Sheet #26D: Meal Obligations for H-2A Employers | U.S. Department of Labor (dol.gov)
[8] Cap Count for H-2B Nonimmigrants, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, Nov. 16, 2023, Cap Count for H-2B Nonimmigrants | USCIS, (last visited: Nov. 22, 2023).
[9] H-2B Employer Data Hub, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, Jun. 30, 2023, H-2B Employer Data Hub | USCIS, (last visited: Nov. 22, 2023).
[10] H-2B Temporary Non-Agricultural Workers, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, Nov. 22, 2023, H-2B Temporary Non-Agricultural Workers | USCIS, (last visited: Nov. 22, 2023).
[11] Processing Times, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, Processing Times (uscis.gov), (last visited: Dec. 4, 2023).
[12] Chris Fuchs, What is the H-1B visa? NBC News, Mar. 30, 2019, What is the H-1B visa? (nbcnews.com).
[13] Fact Sheet #62W: What is “Portability” and to whom does it apply? U.S. Department of Labor – Wage and Hour Division, Nov. 2016, Fact Sheet #62W: What is “Portability” and to whom does it apply? | U.S. Department of Labor (dol.gov).
[14] Processing Times, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, Processing Times (uscis.gov), (last visited: Dec. 4, 2023).
[15] Second H-1B Visa Lottery Announced for FY 2024, Boundless, Jul. 28, 2023, Second H-1B Visa Lottery Announced for FY 2024 – Boundless, (last visited: Nov. 22, 2023).
[16] The H-1B Visa, Explained, Boundless, The H-1B Visa, Explained – Boundless, (last visited: Nov. 22, 2023).
[17] Hannah Whaley, The Powerhouse Visas for U.S. Businesses: H-1B, H-2A, and H-2B, Eagan Immigration, Nov. 30, 2023, The Powerhouse Visas for U.S. Businesses: H-1B, H-2A and H-2B – YouTube.


